|
|
本文章最後由 draculaxx 於 2016-3-19 04:41 PM 編輯
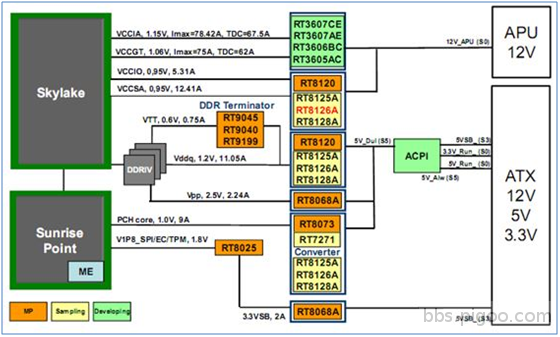
Intel Skylake 晶片組的簡化電源線路示意圖
Understanding All Voltage Configurations from the Motherboard
Intel Processors – Chipset Options
Chipset-related options include all voltages that are not the ones described in the previous page. They include:
A.
North Bridge voltage: This is the voltage that feeds the North Bridge chip from the motherboard chipset. It is important to note that Intel calls the North Bridge chip the MCH (Memory Controller Hub, on motherboards targeted to CPUs without an embedded memory controller), IOH (I/O Hub, on motherboards targeted to CPUs that have an embedded memory controller using a two-chip chipset solution) or PCH (Platform Contoller Hub, on motherboards targeted to CPUs that have an embedded memory controller using a single-chip chipset solution), so the name of this option can vary. PCH chipsets have two separate voltages, VccVcore (usually referred on the motherboard setup as “PCH 1.05 V” or “PCH Voltage,” which is the chip’s main voltage) and VccVRM (usually referred on the motherboard setup as “PCH 1.8 V” or “PCH PLL Voltage,” which feeds the clock multipliers inside the chip).
B.
South Bridge voltage: This is the voltage that feeds the South Bridge chip from the motherboard chipset. It is important to note that Intel calls the South Bridge chip the ICH (I/O Controller Hub). Therefore, the name of the option can vary – “SB Voltage” and “ICH Voltage” are common names.
C.
PCI Express voltage: If you want to change the PCI Express voltage, you will have to study and see where each PCI Express slot or lane is connected on your system. For example, some Intel CPUs can control one x16 or two x8 PCI Express connections for video cards, with the lower-speed slots being controlled by the chipset (PCH). On some other configurations, the PCI Express x16 slots are provided by the North Bridge chip (MCH or IOH) while the lower-speed PCI Express slots are controlled by the South Bridge chip (ICH). The voltage used by PCI Express lanes is usually hard-wired to the chip’s voltage rail and, therefore, are automatically changed when you change the CPU, the North Bridge (PCH/MCH), or the South Bridge voltage, depending on where the lanes are connected to. Some chipsets (most notably Intel X58) have a separate voltage supply for the PCI Express lanes, and on motherboards based on such chipsets, you may find separate configurations for adjusting the PCI Express voltage. For example, “IOHPCIE Voltage” would adjust the voltage from PCI Express lanes controlled by the motherboard North Bridge chip (IOH), while “ICHPCIE Voltage” would adjust the voltage from the PCI Express lanes controlled by the motherboard South Bridge chip (ICH).
D.
PCI Express clock voltage: Some motherboards allow you to increase the voltage from the clock signal used by the PCI Express lanes. This option is called “PCI-E Clock Driving Control” or “PCI Express Amplitude Control.”
原文出處 |
評分
-
4
查看全部評分
-
|